Tools and Strategies Used |
- Beginning in 2002, PSI initiated a process to address the issue of leftover paint. The process was intended to be collaborative from start to finish. PSI used the following strategy to foster collaboration:
- Established the Paint Product Stewardship Initiative (PPSI) and its goals through a consensus process.
- Developed a detailed work plan during the first year
- Crafted a Memoranda of Understanding (MOU) to define purpose and scope of the project; goals and objectives; and commitments by stakeholders.
- Set-up smaller groups to focus work on specific projects.
- PSI provided agenda and background materials prior to meetings and calls; meeting and calls were summarized and participants had opportunities to comment
- The PPSI fostered collaboration with specific tools:
- Monthly PPSI briefing conference calls
- PPSI conferences (once or twice a year)
- PSI Website featuring status of projects, reports, and posting of agenda, participant lists, meeting/call presentations, and meeting/call minutes
|
| |
Effectiveness of Tools/Strategies |
| |
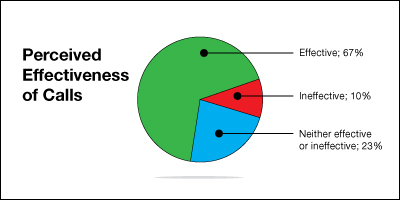
- 67% of PPSI participants indicated that briefing calls were either “effective” or “somewhat effective”
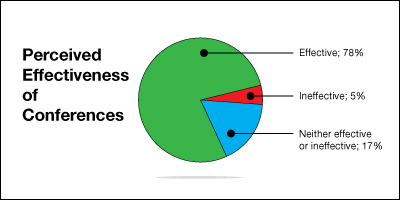
- The survey of PPSI participants asked respondents to indicate how effective they thought the conferences were:
- 78% of participants indicated that PPSI conferences were “very effective,” “effective,” or “somewhat effective.”
|
| |
 |
| |
 |
| |
View of process by different groups |
| |
- Local and federal government respondents had the most positive perception of collaboration, whereas private businesses responded less positively.
- Government representatives were more active participants in terms of call and meeting participation and felt more strongly that collaboration contributed to achieving PPSI goals.
- Those who funded the program attributed more importance to the collaborative effort than those that did not.
- Respondents did not feel significantly torn between meeting the needs of their own organization and the needs for the collaboration. Those working for private companies felt the most hindered.
|
| |
Degree of collaboration |
| |
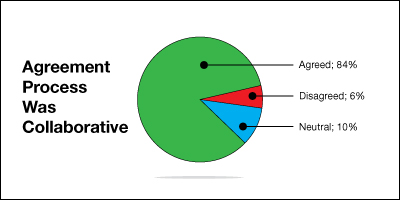
- 84% of PPSI participants “strongly agreed,” “agreed,” or “somewhat agreed” that the PPSI was collaborative
- PPSI participants generally felt that collaboration broke down during the development of legislation in Oregon and during the program planning and implementation stages
|
| |
 |
| |
|
| |
| |




